Introduction:
We use programming language to build applications that we use in our work and domestic lives. This is true for almost every computer application that we use. There are numerous languages out there, that are at the disposal of the programmers that use them for various purposes. The language that is used to add more functionality to MS Office, or is used as a default programming language for MS Office is called Visual Basic for Application or simply VBA.
Excel being part of the MS Office suite uses the same programming language and we often found functions and macros written in this language in our excel worksheets. Such written functions are called User Defined Functions, similarly code written to automate the task in Excel are called Macros.
In today’s tutorial we will explore what is VBA, its different features, a brief introduction to VBA programming and more.
Accessing the VBA Window in MS Excel:
As we move on to use Excel VBA, the first thing is see where we have this programming option in Excel. The easiest way of accessing the code editor window in excel is to press Alt+F11 while you are using an Excel worksheet. Alternatively see How to Open Excel VBA Editor
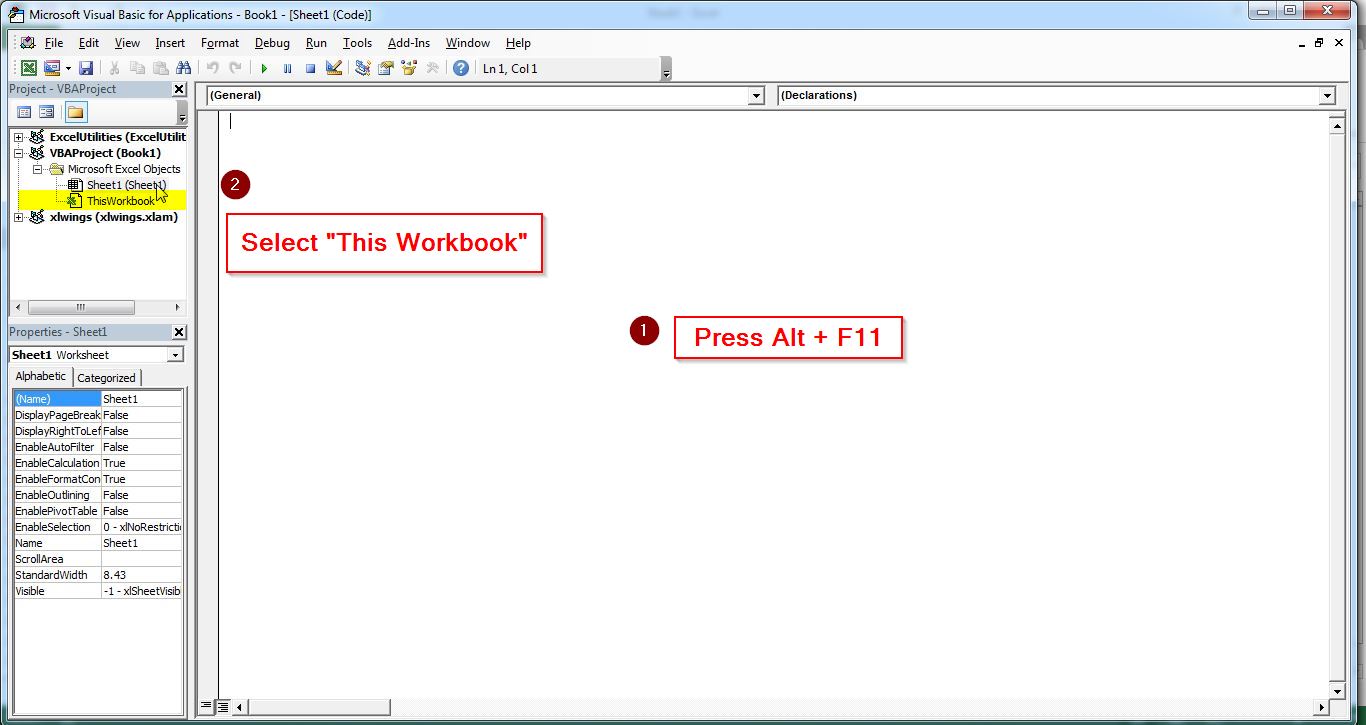
This is the window where we will put all the macros and the functions.
Classification of codes used in MS Excel VBA:
The code we write in VBA can be classified in either of the following three categories:
User Defined Function:
Excel has numerous functions that can be used as we need them. Out of these functions, we came across the situation where neither of them fits in or the formula based solution is too complicated to use, we revert to this option.
We revert to writing function that fulfill a situational or a a very specific need. For example consider following set of code that is written to find the if value is less then zero, is zero or more then it:
Function FindSign(number)
Select Case number
Case Is < 0
FindSign = “-ive”
Case 0
FindSign = “Zero”
Case Is > 0
FindSign = “+ive”
End Select
End FunctionNote that the function always start with “Func” that is used to show its a function. In the above example of function, we have used a special command called “Case” to find if a number is less then zero (or negative), equal to zero or is positive (greater then zero). This is just a start-up example of function that can be easily written with IF() statements, but, we can produce really complicated functions as well.
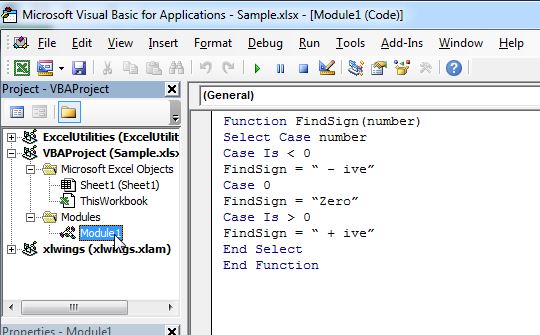
In order for these functions to work, we need to place them in “Modules”. A module can be placed or inserted in a worksheet when we have VBA windows enabled. One need to go to Insert > Module and click to insert the module. Once inserted we will select it and place the function code there.
Once we have done this, we will be able to access the function from functions window.
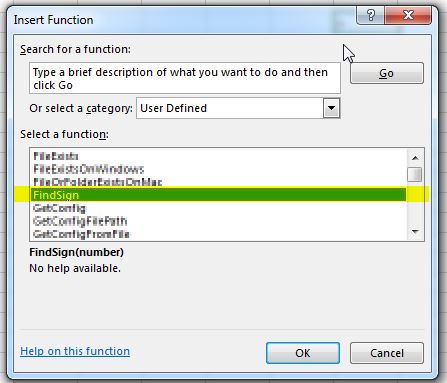
Thus a user can write any thing he wants to be used a User Defined Function.
The Macros:
Macros also belong to the VBA family and are used to automate the task that are frequently done by a user. Thus they are used to speed up the work and reduce burden on end users. An example of already incorporated macros in MS Office is the option to save file after certain time period. Thus certainly reduced the burden on user and also reduces the chances of loosing data if file is not saved.
Besides this, there are numerous situations where VBA is a must required. Consider following example of vba that will highlight all cells that contains formulas in the range:
Sub CellWithFormulas()
Dim Dataset As Range
Set Dataset = Selection
Dataset.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeFormulas).Interior.Color = vbRed
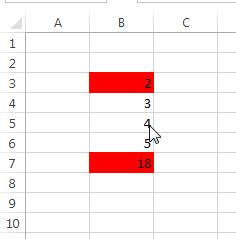
End SubThe macros is placed in the same module where we have placed the function. When we execute this macro from the developer’s tab, we have following result:
In this example, cell B3 and B7 contains the formulas.
Event Procedures:
As is indicated by the name, these are the codes that are meant to be used when something or some event happens. The example of an event could be the opening of a workbook, inserting a number in a cell, clicking some cell and many more.
Events Procedures are useful as they are active behind the scene are run as something happens. A very useful example of even procedure is one that is used to highlight the row and column as active cell changes. This makes reading and tracking the data very easy.
Private Sub ActiveCellHighlight(ByVal Target As Range)
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Cells.Interior.ColorIndex = 0
Target.Interior.ColorIndex = 6
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
End SubThe result is a highlighted active cell.
Debugging your code?
The code that a user writes is not always correct and contains errors. In this case we need a debugging mechanism to find the mistake that we have done. For such situation, VBA editors provides us with a handy tool called “Immediate Window”.
This window can be accessed by using key Ctrl + G when VBA editor is active. This window can be used to execute a line of code, to get the information related to the worksheets, set values to the variables and run macros.
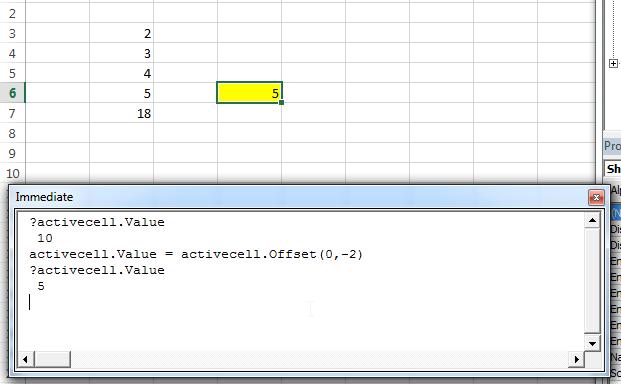
For example in the following screen shot, the initial value of the active cell with yellow fill was 10, as we have found by command ?activecell.value. The value is then re-assigned by using the assignment operator and the offset command.
The offset command lets the value to be on the left side of the cells at difference of 2 columns (hence the negative sign: -2). and when we reprint the value of active cell, it is 5.
In the same way, this can be used to run macros, testing small snipts of vba and much more.
Conclusion:
VBA is a very handy tool for excel users and gives them a lot of control over their worksheets. The use of VBA makes worksheets look more professional and more interactive. Please download the attached file for example and the vba code.